First of all, some review...
What do you remember about organelles?
What do you remember about organelles?
Which organelle converts glucose into energy?
A) Nucleus
B) Ribosome
C) Mitochondria
D) Vacuole
Which organelle transports materials?
A) Endoplasmic reticulum
B) Golgi body
C) Cytoplasm
D) Vacuole
What does a plant cell have that animal cells don’t have?
A) Vacuole
B) Nucleus
C) Mitochondria
D) Cell wall
What do ribosome do?
A) Package materials
B) Photosynthesis to create glucose
C) Creates proteins
D) Controls the cell
Then we started on the new topic
Learning Goals: Understand how diffusion and osmosis moves materials within cells.
Success Criteria: You can describe diffusion and osmosis using proper terminology.
Here are the notes I gave in class.
Diffusion
Concentration: how many particles are in one area.
High concentration: a lot of particles in one spot.
Low concentration: a few particles in one spot.
Diffusion is when particles move from high
concentration to lower concentration areas.
This is how nutrients move inside your cells.
Osmosis
Movement of water across a membrane.
Solution: Water with particles dissolved in it.
Solute: the particles in the water. (example: salt)
Osmosis: When water moves across a membrane towards the side with more solutes.
Osmosis
demonstration
Day 1
Day 2 Day3
Carrot A: 7.23 g
Carrot B: 7.41 g
(salt)
Hypothesis:
Carrot B should get lighter (hypertonic).
Carrot A should get heavier (hypotonic).
-----------------------------------------------------
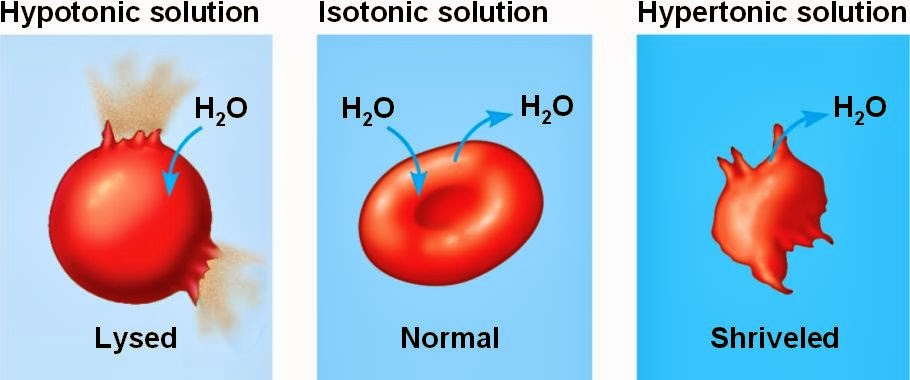
Hypertonic: More solutes outside the cell. The cell shrinks.
Hypotonic: Less solutes outside the cell. The cell grows.


No comments:
Post a Comment